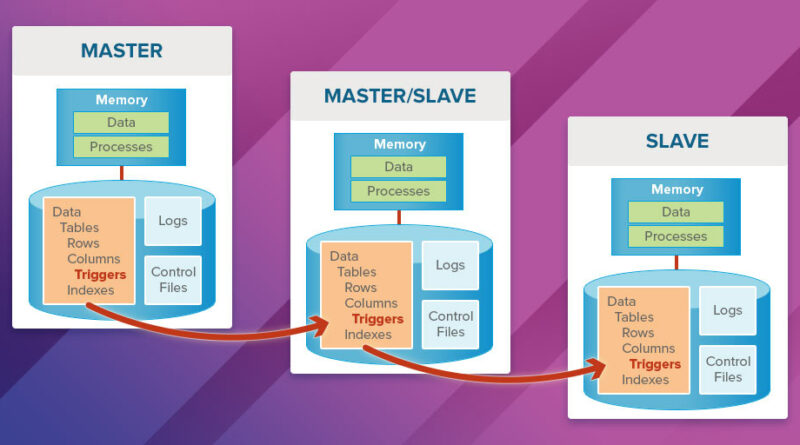
How to Set Up MySQL Master-Slave Replication (Step by Step)
MySQL replication allows you to copy data from one MySQL server (the master) to one or more MySQL servers (the slaves). This guide will walk you through the process of setting up Master-Slave replication step-by-step on two Linux servers.
📋 Prerequisites
- Two MySQL servers installed (MySQL 5.7 or newer)
- Basic knowledge of Linux command line
- Root or sudo access on both servers
- Unique server IDs for each MySQL instance
🔧 Step 1: Configure the Master Server
1. Edit the MySQL Configuration File
Open the configuration file on the master server (e.g., /etc/mysql/my.cnf or /etc/my.cnf):
[mysqld]
server-id=1
log_bin=/var/log/mysql/mysql-bin.log
binlog_do_db=your_database_nameReplace your_database_name with the actual name of the database you want to replicate.
2. Restart MySQL Service
sudo systemctl restart mysql3. Create a Replication User
mysql -u root -p
CREATE USER 'replicator'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'yourpassword';
GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'replicator'@'%';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;4. Get Master Log File Information
FLUSH TABLES WITH READ LOCK;
SHOW MASTER STATUS;Note down the File and Position values. Leave this terminal open to keep the lock.
🗂 Step 2: Backup and Transfer the Database
mysqldump -u root -p --all-databases --master-data > master_dump.sqlTransfer the file to the slave server:
scp master_dump.sql user@slave_ip:/tmp/📥 Step 3: Configure the Slave Server
1. Edit the MySQL Configuration File
Edit the /etc/mysql/my.cnf file on the slave server:
[mysqld]
server-id=2
relay_log=/var/log/mysql/mysql-relay-bin.log2. Restart MySQL on the Slave
sudo systemctl restart mysql3. Import the Dump File
mysql -u root -p < /tmp/master_dump.sql4. Configure Replication on Slave
Use the master status info from Step 1:
CHANGE MASTER TO
MASTER_HOST='master_ip',
MASTER_USER='replicator',
MASTER_PASSWORD='yourpassword',
MASTER_LOG_FILE='mysql-bin.000001',
MASTER_LOG_POS= 107;5. Start the Slave
START SLAVE;6. Check the Slave Status
SHOW SLAVE STATUS\GEnsure that Slave_IO_Running and Slave_SQL_Running are both set to Yes.
✅ Step 4: Verify the Replication
- Make a change (insert/update) on the master database.
- Check if the change appears on the slave.
📌 Tips and Best Practices
- Use
skip-name-resolveto speed up connection resolution. - Use different server IDs for all MySQL servers in your environment.
- Secure your replication user account and limit access.
- Enable monitoring and alerting for replication lag or failure.
📚 Troubleshooting
If replication fails, use the following:
SHOW SLAVE STATUS\G– check for errors inLast_ErrorSTOP SLAVE; RESET SLAVE ALL;– to reset and retry replication setup- Check firewalls, ensure port 3306 is open
🎉 Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve successfully set up MySQL Master-Slave replication. This setup can help with read scaling, backups, and disaster recovery. Be sure to monitor your setup regularly and keep both servers up to date.