How to Optimize MySQL Performance (Step-by-Step)
Optimizing MySQL performance is crucial for ensuring responsive applications and efficient use of server resources. This guide walks you through essential techniques and configuration tips to improve your MySQL server’s performance step by step.
🚀 Step 1: Enable Slow Query Log
First, identify slow and inefficient queries by enabling the slow query log:
[mysqld]
slow_query_log = 1
slow_query_log_file = /var/log/mysql/slow.log
long_query_time = 2Restart MySQL:
sudo systemctl restart mysql🔍 Step 2: Analyze Slow Queries
Use the mysqldumpslow or pt-query-digest tool to analyze the slow log:
mysqldumpslow /var/log/mysql/slow.logOr use Percona Toolkit:
pt-query-digest /var/log/mysql/slow.log🧠 Step 3: Use Proper Indexing
- Use
EXPLAINbefore SELECT queries to identify table scans. - Create indexes on columns used in WHERE, JOIN, ORDER BY, and GROUP BY clauses.
CREATE INDEX idx_column ON your_table(column_name);⚙️ Step 4: Tune MySQL Configuration
Edit my.cnf (or my.ini) to optimize these parameters:
[mysqld]
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 1G
query_cache_type = 1
query_cache_size = 64M
tmp_table_size = 64M
max_connections = 200Adjust sizes based on your server’s RAM.
📁 Step 5: Optimize Database Schema
- Use appropriate data types (e.g.,
INTinstead ofVARCHARwhere possible). - Normalize tables, but avoid excessive joins.
- Remove unused columns and tables.
📈 Step 6: Monitor Performance
Use tools like:
- MySQL Workbench – performance reports
- Percona Monitoring and Management (PMM)
- Netdata or Grafana + Prometheus
🧹 Step 7: Regular Maintenance
- Run
ANALYZE TABLEto update index statistics. - Use
OPTIMIZE TABLEto defragment tables.
OPTIMIZE TABLE your_table;
ANALYZE TABLE your_table;💡 Bonus Tips
- Use connection pooling in your app (e.g., MySQLi or PDO with persistent connections).
- Keep MySQL up to date with the latest stable release.
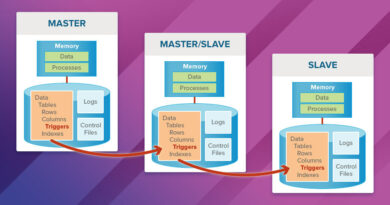
- Offload reads to replicas if using replication.
✅ Conclusion
Optimizing MySQL performance isn’t a one-time task—it’s a continuous process. By identifying slow queries, tuning your configuration, using indexes properly, and keeping an eye on server health, you can dramatically improve your MySQL database’s efficiency and responsiveness.